As Singapore's central bank, MAS aims to promote sustained non-inflationary economic growth, and a sound and progressive financial centre | 
|
Functions of MAS

Conduct Monetary Policies | 
Promote Singapore as a financial centre to the world | 
Supervise and regulate the banks | 
Issue currency |
Financial Supervision and Regulation by MAS in Singapore
| Supervision | Monitoring and assessing a Financial Institution's risk profile and management, governance, financial strength, regulatory compliance and conduct. |
| Regulation | Establishment of specific rules for Financial Institutions by creating and applying legally enforceable rules such as legislations, directions and notices. |
| MAS Supervisory Approach | 6 Key Tenets |
Outcome Focused MAS has to uphold sound regulation of a high standard and exercise appropriate judgment to ensure good regulation outcomes can be achieved. | Shared Responsibility Good regulatory outcomes are most effectively achieved when all stakeholders - MAS, financial institutions, investors and consumers, each taking on specific responsibilities for and shared ownership. | Risk Appropriate MAS should be able to exervise supervisory judgment where justifiedin the particular circumstances of an inpidual financial institution or transaction. |
Responsive to Change and Cycles Regulatory framework has to be reviewed and updated to keep pace with changes in the industry, technological innovation and as new risks emerge. | Impact Sensitive
Regulation should be designed with due regard to its market and cost impact so that it is not unduly burdensome whilst maintaining a high standard consistent with established international standards and practices.
| Clear and Consistent
Regulation should be clear so that financial institutions have certainty and predictability as to their legal obligations.
|
MAS Regulatory Instruments | MAS has different categories of regulatory instruments which are differentiated by their legal effects |
Act Statutory laws under MAS' purview which are passed in parliament and have force of law. e.g. Banking Act | Subsidiary Legislation Provisions of an Act which are spelt out in greater detail and have legal effect. e.g. Banking and Charge Card Regulations |
Directives / Notices Detail specific instructions given to banks to ensure adherence of the specific regulation and have legal effect. e.g. Notice 626 - Prevention of Money Laundering and Countering Financing of Terrorism | Guidelines / Codes / Circulars / Policy Statements Best practices which largely do not have legal effect. e.g. Code of Conduct for Credit Rating Agency |
Main Legislations under Purview of MAS
| Banking Act | Governs the licensing and regulation of banks, merchant banks and related institutions, including their credit card and charge card business. |
| Financial Advisor Act (FAA) | Governs the regulation of financial advisers in Singapore, including their representatives and supervisors. |
| MAS Act | Governs the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and gives it the authority to regulate the financial services sector in Singapore. |
| Securities and Futures Act (SFA) | Governs the regulation of activities and institutions in the securities and derivatives industry, including leveraged foreign exchange trading of financial benchmarks and of clearing facilities. |
| Payment Services (PS) Act | Governs the regulations of payment systems and payment service providers in Singapore |
When Public Loses Confidence in Banks
Banks will have difficulty fulfilling its role of channeling funds from "savers" to "borrowers" when confidence in banks are eroded.
"Savers" will not only stop depositing money into the bank, they might even withdraw money from the bank en-masse. When that happens, it will not only threaten the solvency of the bank, the fear may spread to other banks and thus impacting the safety and soundness of the banking sector.
Did You Know?A bank run occurs when many customers of a bank withdraw their deposits due to fear of the bank's probability of bankruptcy.
In extreme cases, the bank may not have sufficient funds to cover the withdrawals. | 
|
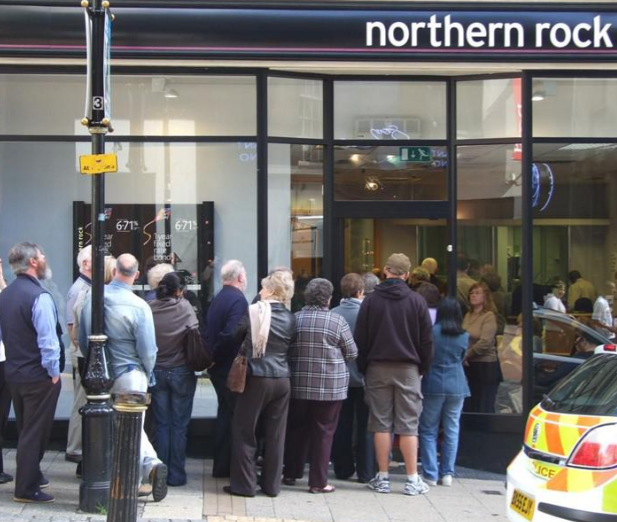
Northern Rocks main businesses were collecting deposits and disbursing home loans in UK.
In the mid 2000s, it started to engage in short-term landing. When subprime market showed signs of stress, Northern Rock started to run out of cash.
Media ran reports of Northern Rock's liquidity difficulties.
On 13 September 2007, the UK witnessed its first bank run in 150 years.
|  |
Protection for Singapore Deposits by Singapore Deposit Insurance Corporation Limited (SDIC)
• SDIC administers an insurance scheme for depositors known as the Deposit Insurance Scheme.
• If a member bank fails, each saver will have all his/her deposits aggregated and insured up to $75,000.
• Monies placed with member bank under the CPF Investment Scheme (CPFIS) and CPF Retirement Sum Scheme (CPFRS) are aggregated and separately insured up to $75,000.
• With the new $75,000 limit, more than 90% of insured depositors are covered in full.
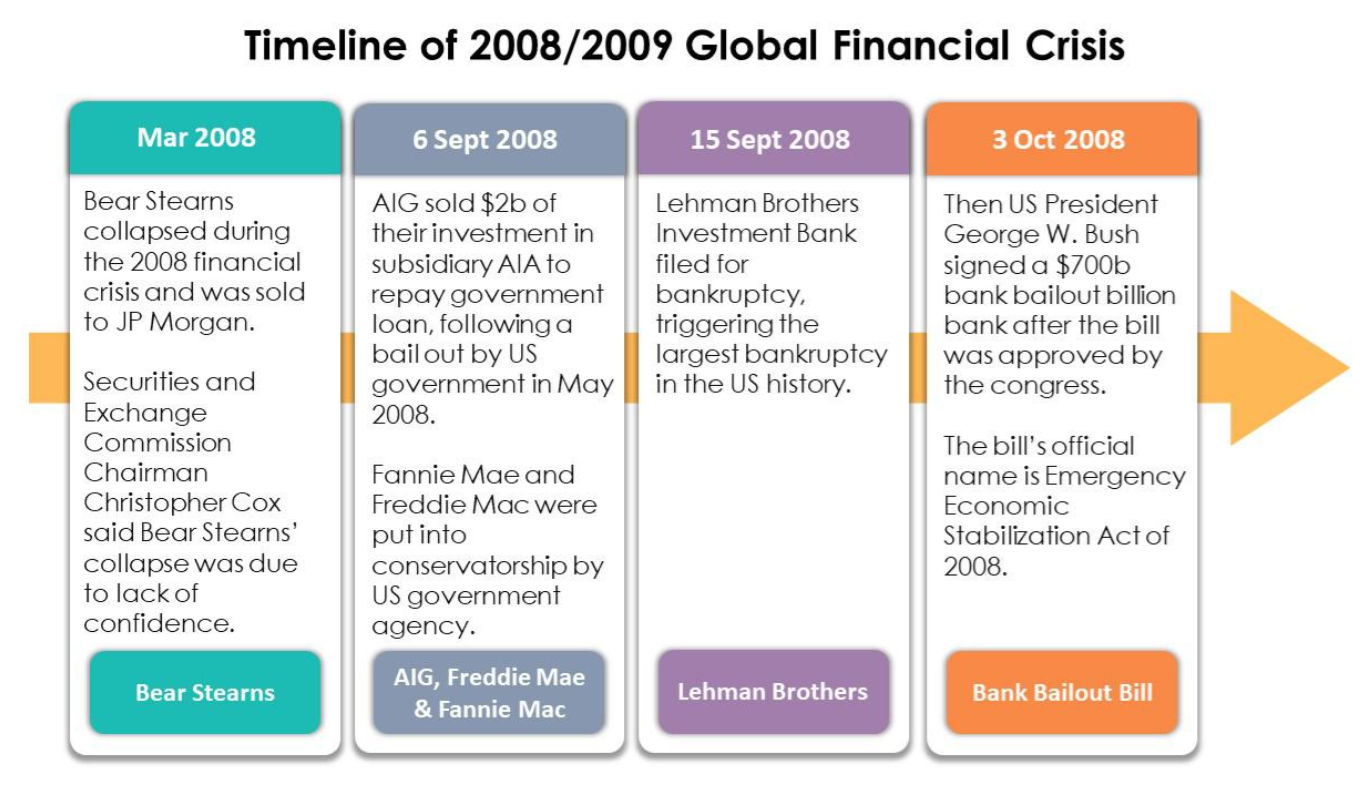
Did You Know? Global Financial Crisis (GFC), also commonly known as sub-prime crisis, was triggered by a series of failures of the financial institutions following the collapse of property markets and short-term loan markets.
While September 2008 witnessed the near failure of AIG, the federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, the defining moment of GFC is Lehman Brothers' bankruptcy.
GFC triggered the worst global economic crisis in 2008/2009. | 
|
Regulation and Supervision of Banking Sector After Global Financial Crisis
• After the Global Financial Crisis, supervisors/regulators believed that it is important to strengthen regulation of the banking sector to prevent another financial crisis of this magnitude.
• Regulators recognized the interconnectedness of the global financial markets, and thus collaborated in the implementation of the regulatory reforms.
• Regulators globally adopted an internationally agreed set of measures to strengthen the regulation, supervision and risk management of the banks.
• Banks operating in Singapore, under the supervision and regulation of MAS, have also implemented the same set of measures agreed internationally.
Did You Know? Singapore, a global financial centre and key trading hub, will inevitably be exposed to money laundering (ML) and terrorist financing risk (FT).
Thus, MAS has put in place robust preventive measures such as Notice 626 to combat ML/FT risks. Banks, at the front line, must remain vigilant to prevent Singapore banks from being accessory to these financial crimes. |  |
MAS and Financial Innovation
• Financial innovation is an integral part of Singapore’s drive to be a smart nation.
• Being mindful of both the benefits and risks that financial innovation can bring, MAS launched a series of initiatives and platforms to collaborate with various stakeholders to better understand the latest financial products, services and technologies.
• Among the many initiatives undertaken by MAS are setting up of a Regulatory Sandbox for banks and fintech companies to experiment new products or technologies, organizing Fintech Festivals annually and establishing an innovation centre to support the vibrancy of Fintech ecosystem.
Click here to find out more about Fintech and Innovation in Singapore.

 Overview
Overview

















